A sequence lock for passing message from a single writer thread to multiple reader threads. The readers are non-blocking, so the writer can always store. Avoids the problem of writer starvation.
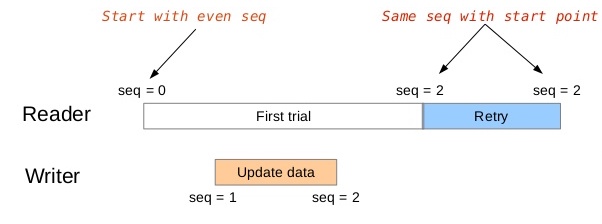
The seqlock is based on an atomic sequence that is increamented during store operations. At the beginning of the store, the sequence is increamented by one to an odd value. After the store is completed, the sequence is increamented by two to an even value.
The reader confirms that the sequence value is the same as when it started, and it confirms that the value is an even sequence. An atomic thread fence is used to prevent tearing on the read and write operations.
The full list of template arguments are as follows:
Type: Must be default constructible and must be copy assignable.
Methods
-
void value_type load(value_type& output) const noexcept(Seq_NoThrow<T>);Load stored value from multiple reader threads.
-
void store(const value_type& input) noexcept(Seq_NoThrow<T>);Store a value from a single writer thread.
These benchmarks were taken on a (4) core Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9300H CPU @ 2.40GHz with isolcpus on cores 2 and 3. The linux kernel is v6.10.11-200.fc40.x86_64 and compiled with gcc version 14.2.1.
Most important aspects of benchmarking:
- Have at least one core isolated with isolcpus enabled in Grub.
- Compile with -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
- Pass isolated cores ID number as an executable argument i.e. ./Seqlock-Benchmark 2 3
| Operations per ms |
|---|
| 149,457 |
To build and install the shared library, run the commands below.
$ mkdir build && cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
$ sudo make install
Inspiration came from these sources. I recommend checking them out:
This software is distributed under the GNU license. Please read LICENSE for information on the software availability and distribution.